Illustration of the static dependence graph used by Diver
How Diver Works
The core technique of Diver is the trace-pruning algorithm based on a fine-grained static dependence graph. This page illustrates the Diver dependence graph with an example Java program as follows.
Example Program
/* example code for Diver */
public class A {
static int g; public int d;
String M1(int f, int z) {
int x = f + z, y = 2, h=21;
if (x > y) {
M2(x,y);
}
int r = new B().M3(h,g);
String s = "M3 retval: " + r;
return s;
}
void M2(int m, int n) {
int t = m - d;
if (t > 0) {
n = g/t;
}
boolean b = C.M5(this);
//System.out.println(b);
}
}
/* example code for Diver */
public class B {
static short t;
int M3(int a, int b) {
int j = 0;
t = -250;
if ( a < b ) {
j = b - a;
}
return j;
}
static double M4() {
int x = A.g, i = 5;
try {
A.g = x/(i+t);
new A().M1(i, t);
}
catch(Exception e) { }
return x;
}
}
/* example code for Diver --- this is the entry class */
public class C {
static void __link() {
Diver.EAMonitor.__link();
}
public static boolean M5(A q) {
long y = q.d;
boolean b = B.t > y;
q.d = 2;
return b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 0, b = -3;
String s = new A().M1(a,b);
double d = B.M4();
String u = s + d;
System.out.println(u);
}
}
the Diver dependence graph of the Example Program above
Data-dependence edges are labeled with the associated variables and the edge types separated with a colon. The data-dependence edge types are:
- p -- parameter edge
- r -- return edge
- h -- heap edge
Control-dependence edges are not labeled. Yet, line styles are used in this illustration to distinguish data and control dependencies:
- solid line -- interprocedural data dependence edge
- dashed line -- interprocedural control dependence edge
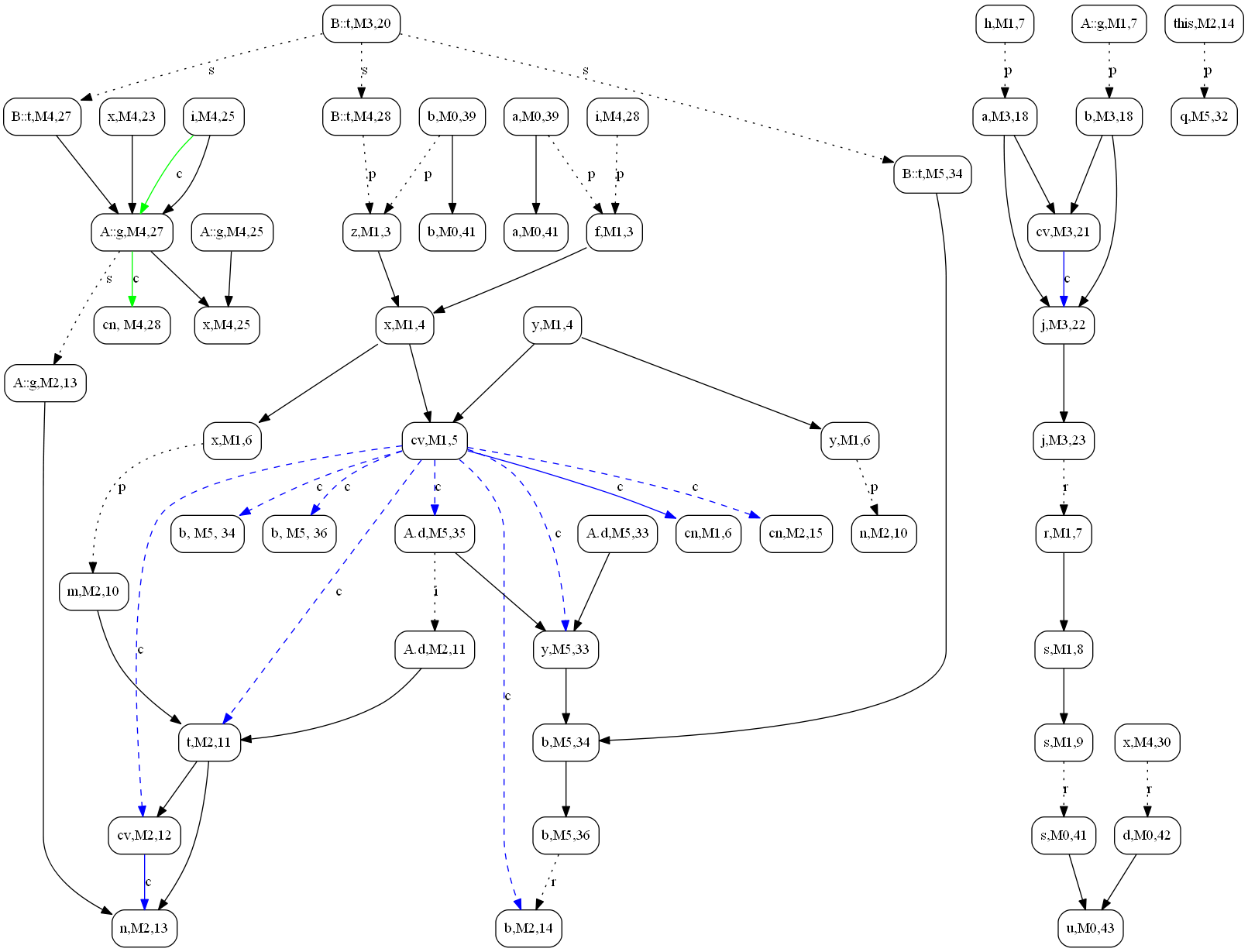
- Note:
- This diagram is a conceptual illustration only;
- The actual dependence graph that Diver created and used for impact analysis is based on the Soot Jimple IR (an immediate representation of Java code transformed from the Java byte-code).
 1.6.1
1.6.1